Definition of Automated Intelligence, Automation, and AI
What is Automated Intelligence?
Automated intelligence refers to integrating automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to create advanced systems capable of performing tasks independently with minimal human input. These systems utilize cutting-edge algorithms, robust data processing methods, and machine learning models to analyze information, identify patterns, and adapt their actions accordingly. By mimicking and often enhancing human decision-making, they deliver faster, more accurate, and context-appropriate results.
The fusion of automation and AI offers numerous benefits. Automated intelligence enables organizations to optimize operations, minimize human errors, and boost efficiency across various sectors. These systems are designed to enhance productivity, from streamlining repetitive tasks and improving resource allocation to generating real-time insights for complex decisions. Moreover, they allow businesses to shift human effort toward strategic and creative endeavors, driving innovation and sustainable growth.
This blend of automation and AI transforms the manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and logistics industries. By harnessing intelligent algorithms to interpret data and make informed decisions, these systems redefine the potential of machines. The outcome is a more efficient, adaptable, and dynamic approach to addressing challenges, representing a significant step forward in technological advancement. As automated intelligence evolves, it unlocks new opportunities, redefining how humans and machines work together in a rapidly changing world.
What is Automation?
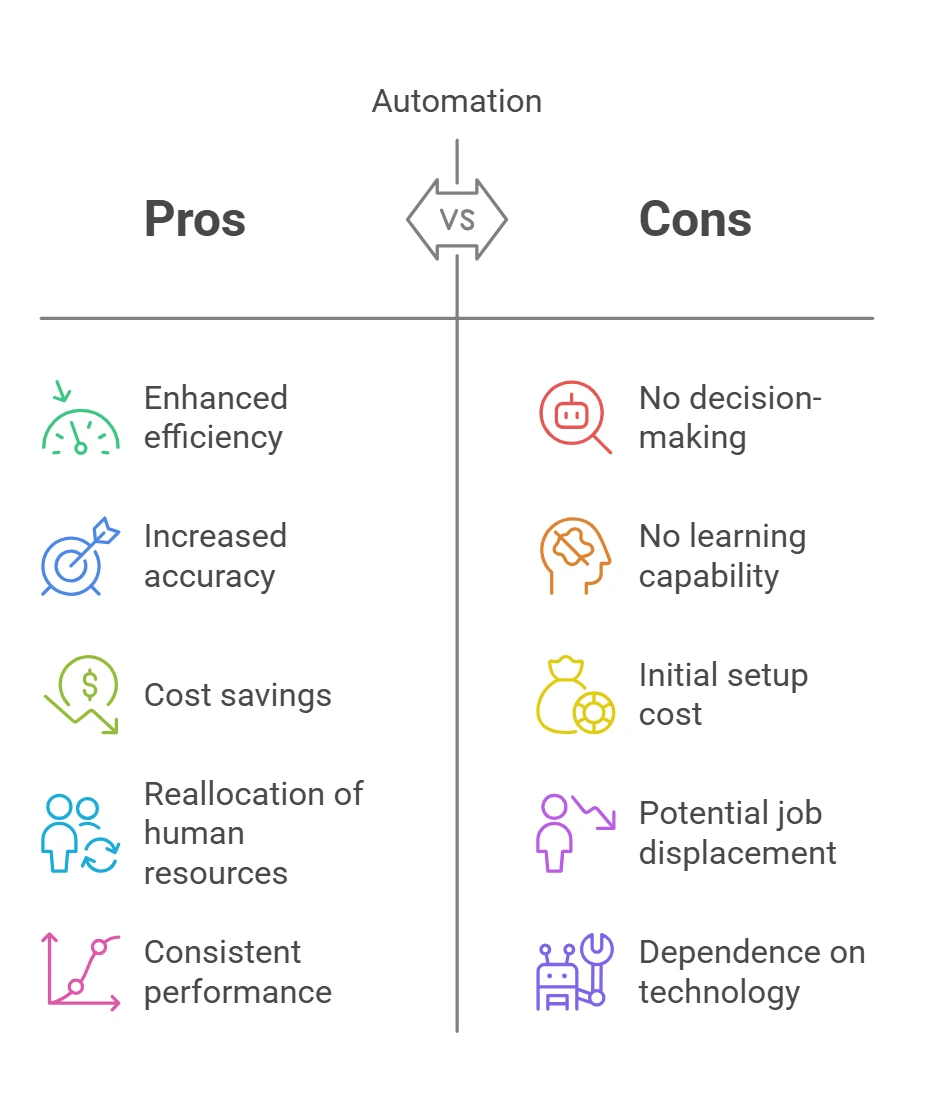
Automation uses technology to perform repetitive tasks based on predefined rules, allowing these processes to operate without human intervention. Its primary purpose is to enhance efficiency and accuracy, ensuring tasks are completed faster and with fewer mistakes. Automation is widely used across industries such as data entry, manufacturing, and workflow management, where precision and consistency are critical.
By following set rules and instructions, automation systems carry out tasks reliably and consistently. For example, in data entry, automation tools can extract information from documents and input it into databases, minimizing the risk of errors. In manufacturing, automated machinery can assemble products or manage inventory with greater speed and accuracy than manual processes. In workflow management, automation ensures that tasks are executed in the correct sequence, reducing delays and increasing overall productivity.
The predictable nature of automation makes it a valuable asset for industries that depend on uniform handling of repetitive tasks. Although these systems do not typically involve decision-making or learning, their ability to execute detailed instructions enables businesses to save time, cut costs, and reallocate human resources to more strategic or creative roles. As automation technology advances, its applications continue to grow, showcasing its capacity to handle routine tasks efficiently while maintaining high reliability and precision.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) involves programming computers to mimic human thinking and learning. Unlike traditional automation, which strictly follows predefined rules, AI leverages advanced technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing (to comprehend text and speech), and computer vision (to analyze and interpret images). These capabilities enable AI to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns that might escape human notice, and make decisions that improve with experience. AI functions as a dynamic, ever-evolving digital brain rather than a simple rule-following machine.
AI’s ability to learn and adapt makes it a powerful tool in tackling complex, data-driven challenges. For instance, in healthcare, AI algorithms can analyze medical images to detect conditions like cancer with remarkable accuracy. In finance, AI models predict market trends, detect fraud, and optimize investment portfolios. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants have revolutionized customer service, offering personalized support and enhancing user experiences.
While automation executes tasks based on fixed instructions, AI takes a more flexible approach, continuously improving performance through feedback and training. This capacity for growth and innovation enables AI to push beyond traditional boundaries, making it indispensable in an era of rapid technological progress. As AI technologies evolve, they promise to reshape industries, create new opportunities, and redefine how humans interact with intelligent systems.
Comparison Between Automated Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence
Automated intelligence combines automation and AI to create self-sufficient systems. Artificial intelligence focuses on replicating human cognition, emphasizing learning and adaptability. Despite their shared reliance on advanced technologies, the two differ in scope and objectives. Here’s a concise comparison:
Definition:
- Automated Intelligence: Integrates automation with AI to enable autonomous operations.
- Artificial Intelligence: Replicates human thought processes using technologies like machine learning.
Focus:
- Automated Intelligence: Achieves self-reliant systems for efficiency and decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence: Develops systems capable of reasoning, learning, and adapting.
Use Cases:
- Automated Intelligence: Found in robotic process automation and intelligent workflows.
- Artificial Intelligence: Powers chatbots, autonomous vehicles, and predictive analytics.
Complexity:
- Automated Intelligence: Combines predefined rules with AI to enhance automation.
- Artificial Intelligence: Addresses complex problems with self-learning algorithms.
Outcome:
- Automated Intelligence: Optimizes processes and improves decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence: Simulates human-like intelligence and drives creativity.
Both systems are pivotal in modern technology, complementing each other to transform industries. Automated intelligence offers a practical approach to efficiency, while artificial intelligence expands possibilities through continuous innovation.

Aspect of Automated Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence
Definition Automated Intelligence: Integrates automation with AI to enable systems to operate autonomously. Artificial Intelligence: Involves technologies designed to replicate human cognitive processes.
Focus Automated Intelligence: A blend of automation and AI to achieve self-sufficient operations. Artificial Intelligence: Technology that emulates human reasoning, learning, and adaptability.
Use Cases Automated Intelligence: Applied in areas like robotic process automation and intelligent process automation. Artificial Intelligence: Utilized in applications such as chatbots, autonomous vehicles, and predictive analytics.
Complexity Automated Intelligence: Merges rule-based automation with advanced AI features. Artificial Intelligence: Concentrates on solving intricate problems and facilitating continuous learning.
Outcome Automated Intelligence: Aims to improve operational efficiency and optimize decision-making processes. Artificial Intelligence: Focuses on achieving human-like reasoning and fostering creativity.
Understanding Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) and Its Advantages
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) represents a significant leap beyond traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While RPA excels at automating repetitive tasks, IPA infuses artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities, transforming it into a powerful tool for streamlining complex business operations.
Key differentiators of IPA include:
- Cognitive Abilities: IPA systems can “think” and “learn” by incorporating AI technologies like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and predictive analytics. This allows them to Understand and interpret human language and process documents, emails, and customer inquiries with high accuracy.
- Analyze and extract data from various sources: Images, videos, and unstructured text.
- Make informed decisions: Adapt to changing circumstances, identify exceptions, and recommend optimal courses of action.
- Enhanced Adaptability: IPA systems are more flexible and resilient than traditional automation. They can learn and adjust to evolving business rules and processes.
- Handle exceptions and irregularities more effectively.
- Continuously improve their performance based on data analysis.
Advantages of IPA for Businesses:
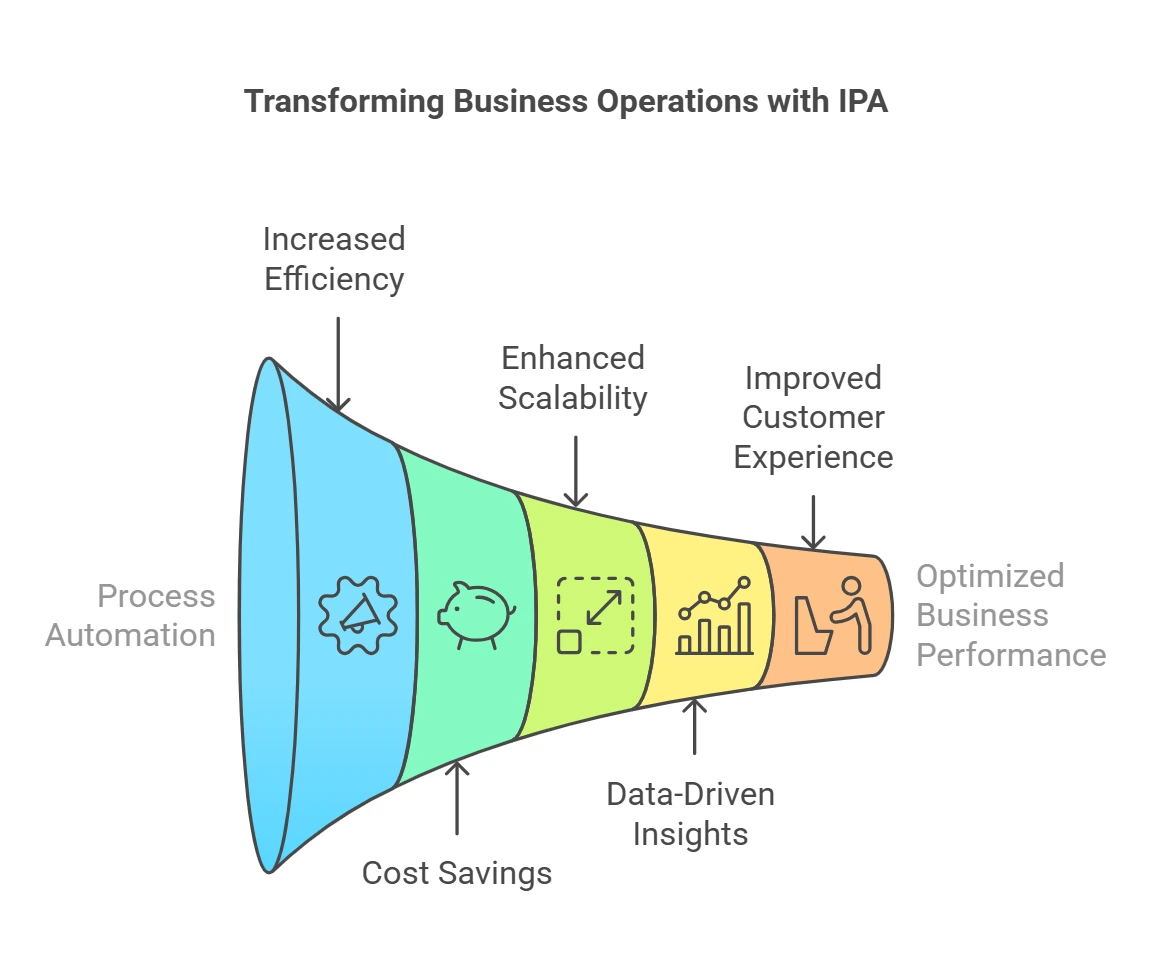
- Dramatically Increased Efficiency: Automates end-to-end processes: Streamlines complex workflows across departments, minimizing manual intervention and reducing bottlenecks.
- Reduces human error: Eliminates repetitive tasks prone to human error, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Increases productivity: Enables employees to focus on higher-value activities such as innovation, creativity, and customer interaction.
- Significant Cost Savings: Reduces operational expenses: Automates labor-intensive tasks, minimizing the need for manual labor and associated costs.
- Optimizes resource allocation: Reallocates human resources to more strategic and impactful roles.
- Improves operational efficiency: Reduces processing times and minimizes delays, leading to cost savings across the organization.
- Enhanced Scalability and Agility: It easily adapts to changing business needs and quickly scales up or down to meet fluctuating demands without significant additional costs.
- Enables rapid response to market changes: Quickly adapts to new regulations, customer demands, and competitive pressures.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides valuable insights: Collects and analyzes data from various sources, providing valuable insights into business processes and performance.
- Enables predictive analytics: Forecasts future trends and identifies potential risks, allowing businesses to make proactive decisions.
- Improves business intelligence: Supports data-driven decision-making across all levels of the organization.
- Improved Customer Experience: Accelerates service delivery: Automates customer service tasks, such as answering FAQs and resolving simple issues, leading to faster response times.
- Enhances customer satisfaction: Provides personalized and consistent customer experiences across all channels.
- Improves customer relationships: Builds stronger customer relationships by providing efficient and practical support.
By leveraging the power of AI, IPA empowers businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and agility. It’s a transformative technology rapidly changing how companies operate across industries.
Five Tools Leveraging Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
Selecting the appropriate tools is crucial for organizations aiming to implement Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) successfully. The following tools are notable for their ability to merge AI and automation, fostering efficiency and innovation:
- UiPath:
- A leading RPA platform that has significantly expanded its AI capabilities.
- UiPath AI Center provides access to pre-built AI skills, including computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning models.
- It allows organizations to integrate these AI capabilities into their automation workflows easily.
- UiPath also offers advanced analytics and reporting features, which provide valuable insights into process performance and identify areas for further optimization.
- Automation Anywhere:
- A cloud-native platform with a strong focus on AI-powered automation.
- It features a powerful AI Fabric incorporating machine learning, natural language processing, and cognitive automation capabilities.
- Automation Anywhere’s platform allows for the creation of intelligent bots to understand and respond to complex situations, such as handling unstructured data and making decisions based on real-time information.
- It also provides advanced analytics and reporting to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the impact of automation initiatives.
- Blue Prism:
- A recognized leader in the RPA market with a strong emphasis on secure and scalable automation.
- Blue Prism’s Digital Workforce platform incorporates AI capabilities like machine learning and cognitive automation.
- It focuses on building intelligent digital workers that can perform various tasks, including data entry, customer service, and financial processes.
- Blue Prism’s platform is known for its robust security features and its ability to integrate with existing enterprise systems.
- Appian:
- A low-code development platform that allows businesses to rapidly design, automate, and improve business processes.
- Appian’s platform incorporates AI capabilities like machine learning and predictive analytics to enhance decision-making and improve process efficiency.
- It enables organizations to build intelligent applications that automate complex workflows, such as customer onboarding, loan processing, and claims handling.
- Appian’s platform is known for its user-friendly interface and ability to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
- Kofax:
- A leading provider of intelligent automation solutions for capturing, managing, and analyzing information across the enterprise.
- Kofax’s platform leverages AI and machine learning to automate document-intensive processes like invoice processing, customer onboarding, and claims handling.
- It offers a comprehensive suite of tools for capturing data from various sources, including paper documents, emails, and mobile devices.
- Kofax’s platform also provides advanced analytics and reporting capabilities to help organizations track key performance indicators and measure the return on investment of their automation initiatives.
By carefully evaluating their needs and requirements, organizations can select the IPA tools that best align with their business goals and drive successful automation initiatives.
This expanded version provides more specific details about each tool’s AI capabilities, highlighting their unique strengths and how they contribute to successful IPA implementations.
Conclusion
Automated intelligence is changing the game for businesses by combining the power of automation and AI to work smarter and faster. With tools like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere, companies can save money, streamline operations, and wow their customers. As tech keeps evolving, jumping on the Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) bandwagon is a must to stay ahead in today’s fast-paced digital world.
See also: How to Use an Artificial Intelligence Death Calculator Effectively.




1 thought on “Unveiling Automated Intelligence: Revolutionizing Business Operations”
Comments are closed.