Introduction
As technology advances, businesses more and more are turning to cloud computing because of its versatility, flexibility, as well as cost-efficiency. But, along with these benefits are significant security issues. Security concerns for sensitive data and to make sure that regulations are in compliance is what has made knowing the security of cloud computing important for organizations regardless of size. This article is designed to give the most comprehensive knowledge of the security features that cloud computing provides and its crucial function in the adoption of cloud-based services, while also protecting against the latest dangers.
Understanding Cloud Computing Security
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security covers the policy, techniques and security measures used to secure data, apps and the infrastructures that are connected to cloud computing. In the ever-changing security landscape, the importance of security practices that are robust cannot be understated. Companies store huge quantities of information on cloud storage, making the cloud a prime target for cyber criminals. Cloud security measures that are effective must be implemented to safeguard private information from access by hackers as well as data breaches and the other risks that could be posed.
Cloud security has multiple aspects, including:
- Secure Data: The security of data in motion and at rest between cloud services and their users is crucial. This requires implementing encryption and access control.
- identity and Access Management (IAM): Ensuring that only authorized users are able to access sensitive information is essential. It involves monitoring the user’s activity as well as managing permissions efficiently.
- Conformity and Regulatory Conformity: Adhering to relevant law and regulations helps protect organizations and increases trust among customers.
Service Models and Their Security Aspects
Cloud computing is typically categorized into three primary service models–Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)–each presenting unique security challenges and delineating responsibilities through the shared responsibility model:
- IaaS: Organizations that use IaaS must ensure the security of their application including data, operating systems. In turn, the cloud service provider is responsible for protecting the infrastructure.
- PaaS: In the PaaS model, the providers usually take care of security on the infrastructure while the customers have the responsibility of managing applications built using the platform.
- SaaS: With SaaS providers, they manage all aspects of the service, which includes the application as well as the data. However, the customers take on the user’s access and rights.
Knowing these models is essential because it allows organizations to understand their obligations, which leads to more effective security plans.
Deployment Models and Considerations
Companies can use cloud computing resources in a variety of ways, including public cloud, private, hybrid and multi-cloud, each requiring a specific security measures.
- Cloud: Public Cloud: Offered by third-party service providers, public clouds can be accessed by multiple users. Businesses that utilize public cloud services must take care of risks that arise from the sharing of data among customers, including the privacy of data and the sovereignty.
- Private Clouds: Exclusively used by one organization cloud services offer opportunities for enhanced security and customization. Yet, the organizations bear the burden of managing cloud’s infrastructure as well as security and privacy controls.
- Hybrid Cloud The model blends cloud services that are private and public which allows for greater flexibility when it comes to the management of data. Security should address the complexity of working in a variety of environments while also ensuring safe data transfers between these.
- Multi-cloud: By utilizing services offered by different cloud providers, companies are able to reduce risks and benefit from different services. However, this strategy could cause issues related to managing, integration, as well as security management.
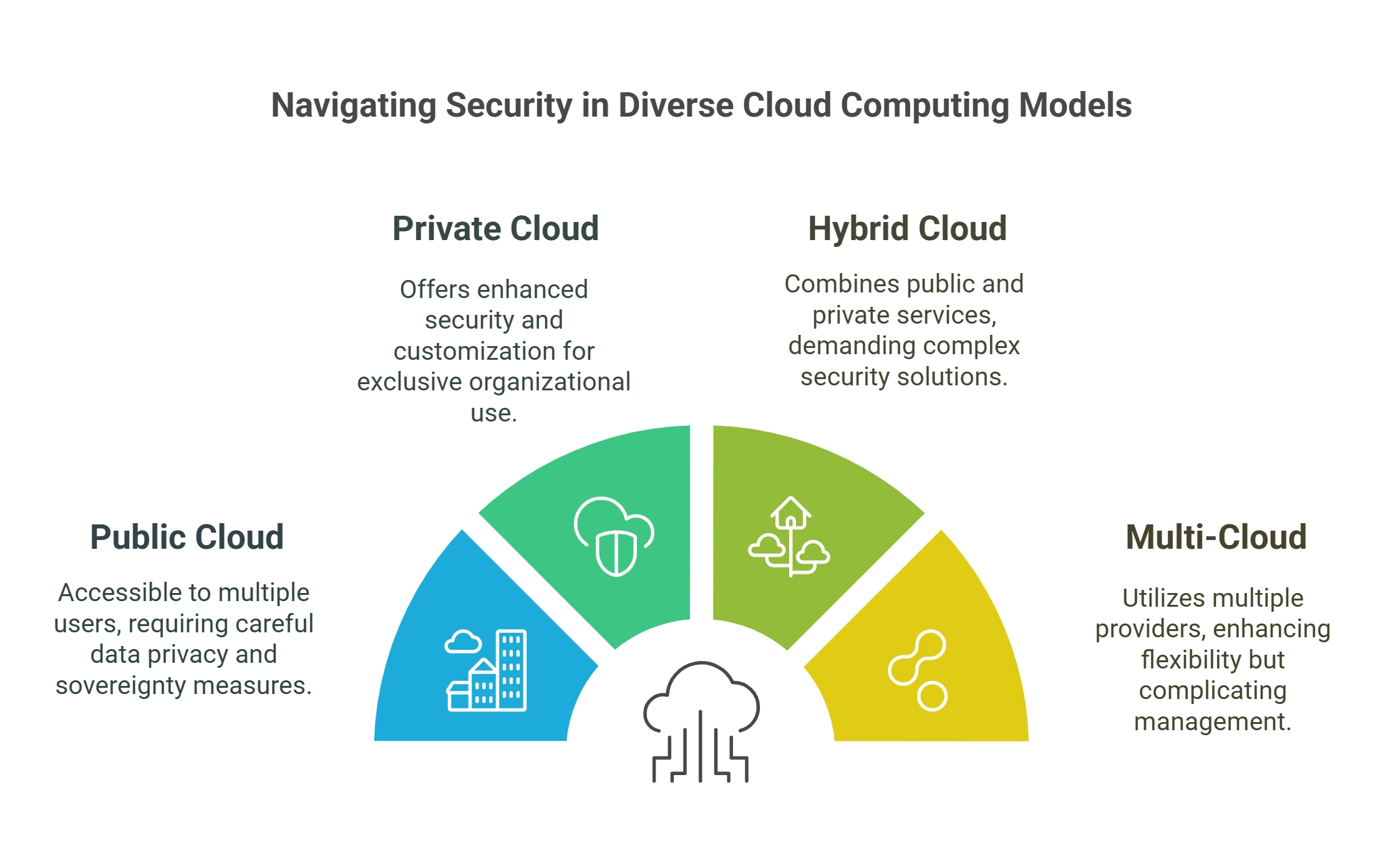
Customizing security policies to specific cloud deployment strategies is crucial to efficient cloud security.
Challenges in Cloud Security and Best Practices
With the growth of cloud-based services increases businesses face numerous security issues. Being aware of these risks and applying the best practices is essential for protecting data while maintaining the control of cloud services.
Common Security Challenges
Cybersecurity threats to cloud environments could manifest themselves as
- Authorized Access Hackers can access confidential data via unauthorised access or stolen credentials. security, resulting in security breaches.
- Data Breach: Misconfigured cloud storage or APIs could expose sensitive data to unauthorised entities, which could pose significant risk to an enterprise.
- Incorrect configurations: Lack of oversight on cloud configurations could cause vulnerabilities. even seemingly small mistakes can lead to security holes.
- Inaccessibility Many organizations lack access to their cloud environment which makes it difficult to identify and react to security issues quickly.
In order to reduce these risks enterprises must adopt an aggressive approach towards cloud security.
Implementing Effective Security Controls
- Implementing Zero-Trust Principles Implementing a zero trust security system ensures a rigorous authentication process for every user regardless of where they are inside or outside of the network. It also prevents unauthorized access to the network and also minimizes movement lateral during an incident.
- Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA offers additional security, as it requires users to submit several forms of authentication prior to getting access to confidential information. This method significantly decreases the risk of access being unauthorized.
- Utilizing encryption: Businesses should ensure that they encrypt sensitive data both at rest and during transport to shield against unauthorized access. Encryption standards that are strong and secure is an essential best practice.
- Utilizing Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP): These tools let organizations analyze the cloud infrastructure for issues and weaknesses, providing insight for improving security.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
The need for real-time monitoring is vital to being able to detect and respond to security issues in cloud-based environments. The establishment of a reliable monitoring system will allow organizations to spot irregularities and suspicious behavior efficiently. The most important elements of a monitoring plan include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions analyse and collect security information in the cloud infrastructure. They provide insight into threats that could be posed and providing timely response to incidents.
- The process of establishing an Incident Response Strategy: An extensive plan for responding to an incident outlines the procedures that the company will follow in the event of a security breach. Regularly scheduled training and games aid staff in becoming familiar with processes, which allows for a rapid and swift response when security breaches happen.
The Future of Cloud Security
The cloud security landscape changes constantly. With the advent of new technology companies must adjust their security practices to meet the new challenges and threats.
Innovations and Advances in Cloud Security
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Incorporating AI and ML in cloud security tools could give valuable insights and improve the capabilities of detecting threats. These tools can spot the patterns that indicate malicious activities, and automate responses to reduce the threat in real time.
- Cloud-Native Application Security Platforms (CNAPP): These platforms are a major step toward integrating security into processes of development, and ensuring security is an integral component of the development process (SDLC). CNAPPs improve both the security of applications as well as cloud infrastructure security, offering a comprehensive view and security.
Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
With more organizations moving to the cloud, remaining in compliance with the regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA is becoming more complex. Cloud compliance involves:
- Understanding Regulatory Requirements Every regulation comes with specific specifications for data storage processing, reporting, and storage. Companies must be aware of the obligations they have to meet in order to remain compliant.
- embedding compliance within cloud Operation: Security-related operations must be in line closely to regulatory standards by integrating compliance checkpoints in workflows. Tools for assessing compliance can aid in reducing the time spent on compliance.
The Role of Education and Awareness
Despite advances in technology yet, human errors remain an important cause of security breaches. Thus, awareness and education is essential:
- Regular training sessions: Organizations should conduct regular training sessions to inform workers on current cyber security threats in the cloud and best techniques. They can identify security risks and take appropriate action.
- Awareness campaigns: Inculcating security consciousness into the mindset through awareness programs can dramatically improve an organization’s security position. A regular communication regarding security news as well as reminders for security can help keep it at the forefront of employees’ minds.
Conclusion
With more and more organizations adopting cloud computing, knowing and implementing efficient security measures has never been more important. Cloud security is essential to safeguard sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and reducing risks. In addressing issues that are common by implementing best practices as well as staying on top of emerging developments, businesses can successfully manage the challenges in cloud security. Cloud security’s future is full of opportunities and innovations However, it’s going to require ongoing commitment and constant monitoring in order to keep a strong security posture and safeguard against the ever-changing threats.



