Introduction
Generative Engine Optimization: The internet has undergone a seismic shift in how information is discovered and accessed. Traditionally, search engines like Google and Bing reigned supreme, guiding users to relevant websites through lists of ranked results. However, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has ushered in a new paradigm: generative engines (GEs). These systems, exemplified by platforms like BingChat, Google’s SGE, and Perplexity.ai, combine conventional search with generative models to synthesize information and provide direct, comprehensive answers to user queries. While this transformation offers unparalleled benefits for users and developers, it poses significant challenges to the third stakeholder in the digital ecosystem: website and content creators.
This article will explore the emerging concept of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a revolutionary approach designed to empower content creators in this new information landscape. GEO aims to ensure that high-quality content remains visible and discoverable within the responses generated by GEs, fostering a healthy and equitable digital ecosystem.
The Rise of Generative Engines and Their Impact
Generative engines represent a fundamental shift in how users interact with information. Unlike traditional search engines that simply provide links to relevant websites, GEs leverage the power of LLMs to:
- Synthesize Information: GEs can gather information from multiple sources, distilling it into a concise and coherent response.
- Provide Direct Answers: Users receive immediate answers without the need to navigate through numerous websites.
- Personalize Responses: GEs can tailor responses based on user context and preferences.
- Attribute Sources: GEs typically cite the sources used to generate the response, allowing users to verify the information.
The benefits of GEs are undeniable. Users gain faster and more accurate access to information, while developers can craft precise and personalized experiences. However, this shift raises concerns about the visibility of original content creators. In a world where GEs directly answer questions, users may have less incentive to visit the original websites that provide the information. This has the potential to drastically reduce organic traffic to websites, impacting the livelihoods of countless businesses and individuals who rely on online visibility.
Introducing Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
To address the challenges posed by GEs, we introduce Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). GEO is a novel framework that enables content creators to optimize their content for visibility within the responses generated by GEs. Unlike traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which focuses on ranking websites in search results, GEO aims to influence how GEs select, interpret, and present information from specific websites.
Key Principles of GEO
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is not merely about adapting existing SEO tactics to a new environment. It represents a fundamentally different mindset focused on empowering content creators to thrive alongside AI-driven information delivery systems. To fully appreciate its potential, a deeper understanding of its core principles is crucial:
- Creator-Centricity: Prioritizing Content Creators’ Control and Sustainability. The primary goal of GEO is to enable content creators to maintain control over how their work is discovered, interpreted, and presented by generative engines. This is vital for ensuring the long-term sustainability of the creator economy. Instead of being at the mercy of opaque algorithms, creators are given the tools and knowledge to actively manage their online presence and impact.
- Black-Box Optimization: Adapting to Proprietary Systems without Requiring Access. Generative engines, especially those deployed by large tech companies, are often closed systems with proprietary algorithms and data. GEO embraces a black-box approach, meaning that optimization strategies are designed to be effective without requiring insider knowledge of the specific inner workings of each engine. This ensures that GEO techniques remain relevant and adaptable as engines evolve and change their algorithms. The black-box nature also promotes broader adoption, as creators don’t need special access or privileged information to implement GEO strategies.
- Flexibility and Customization: Tailoring Strategies to Diverse Content and Goals. The digital landscape is incredibly diverse, with content creators producing everything from news articles and blog posts to product reviews and educational resources. GEO recognizes that a one-size-fits-all approach is insufficient. It provides a flexible framework that allows creators to define their own visibility metrics and tailor their optimization strategies to suit their specific content types, target audiences, and business goals. A local restaurant, for example, might prioritize visibility in queries related to “best pizza near me,” while a research institution might focus on ensuring that its publications are accurately cited in responses about specific scientific topics.
- Ethical Considerations: Promoting Responsible Optimization and Combating Misinformation. With the rise of AI-generated content, it’s crucial to address the ethical implications of optimization. GEO should not be used to manipulate or distort information, but rather to improve the overall quality and accuracy of the content presented by generative engines. Responsible GEO practices prioritize transparency, factual accuracy, and a commitment to serving the user’s best interests. This includes avoiding clickbait, deceptive claims, and any attempt to amplify misinformation or harmful content. The long-term success of GEO depends on building trust with users and ensuring that optimization efforts contribute to a more informed and reliable online environment.
The GEO Framework
The Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) framework provides a structured approach for content creators to improve their visibility within generative engine responses. This framework consists of four interconnected components:
- a) Defining Visibility Metrics: This initial step involves identifying and quantifying the specific factors that determine how prominently and effectively content is displayed within a GE response. Because GEs present information in varied formats (e.g., inline citations, summaries, direct answers), traditional ranking metrics are insufficient. Customized metrics, such as Word Count, Citation Position, and Subjective Impression (detailed later), are designed to capture visibility more accurately. The choice of metrics should align with the content creator’s specific goals (e.g., increasing brand awareness, driving traffic to a website, establishing expertise on a topic).
- b) Content Analysis: Once visibility metrics are defined, the next step involves a thorough analysis of existing website content to identify areas for optimization. This analysis may include:
- Keyword Research: Understanding the search terms that users are employing when seeking information related to the content creator’s niche.
- Style and Tone Analysis: Assessing the readability, clarity, and authoritativeness of the writing style.
- Fact-Checking and Verification: Ensuring the accuracy and verifiability of the information presented.
- Source Attribution: Identifying opportunities to add citations to reputable sources.
- Multimodal Integration: Exploring ways to incorporate images, videos, and other multimedia elements to enhance engagement and visibility.
- Competitive Analysis: Evaluating the content of competitors to identify gaps and opportunities for differentiation.
- c) Implementing Optimization Strategies: Based on the insights gleaned from the content analysis, content creators can implement a range of optimization strategies:
- Content Enhancement: Rewriting or expanding existing content to improve its clarity, accuracy, and relevance.
- Stylistic Alterations: Adjusting the tone and style of the writing to be more persuasive, authoritative, or engaging.
- Keyword Integration: Incorporating relevant keywords strategically throughout the content.
- Structured Data Markup: Using schema markup to provide search engines with more context about the content.
- Citation and Quotation Addition: Adding citations and quotes from reputable sources to enhance credibility.
- Multimodal Content Integration: Incorporating images, videos, and interactive elements.
- d) Evaluation and Refinement: Optimization is an iterative process. Once changes have been implemented, it’s essential to evaluate their effectiveness by tracking the defined visibility metrics. This may involve using analytics tools, monitoring GE responses for relevant queries, and soliciting feedback from users. Based on the evaluation results, content creators can refine their strategies and make further adjustments to improve their visibility over time. This continuous cycle of analysis, optimization, and evaluation is key to achieving long-term success with GEO.
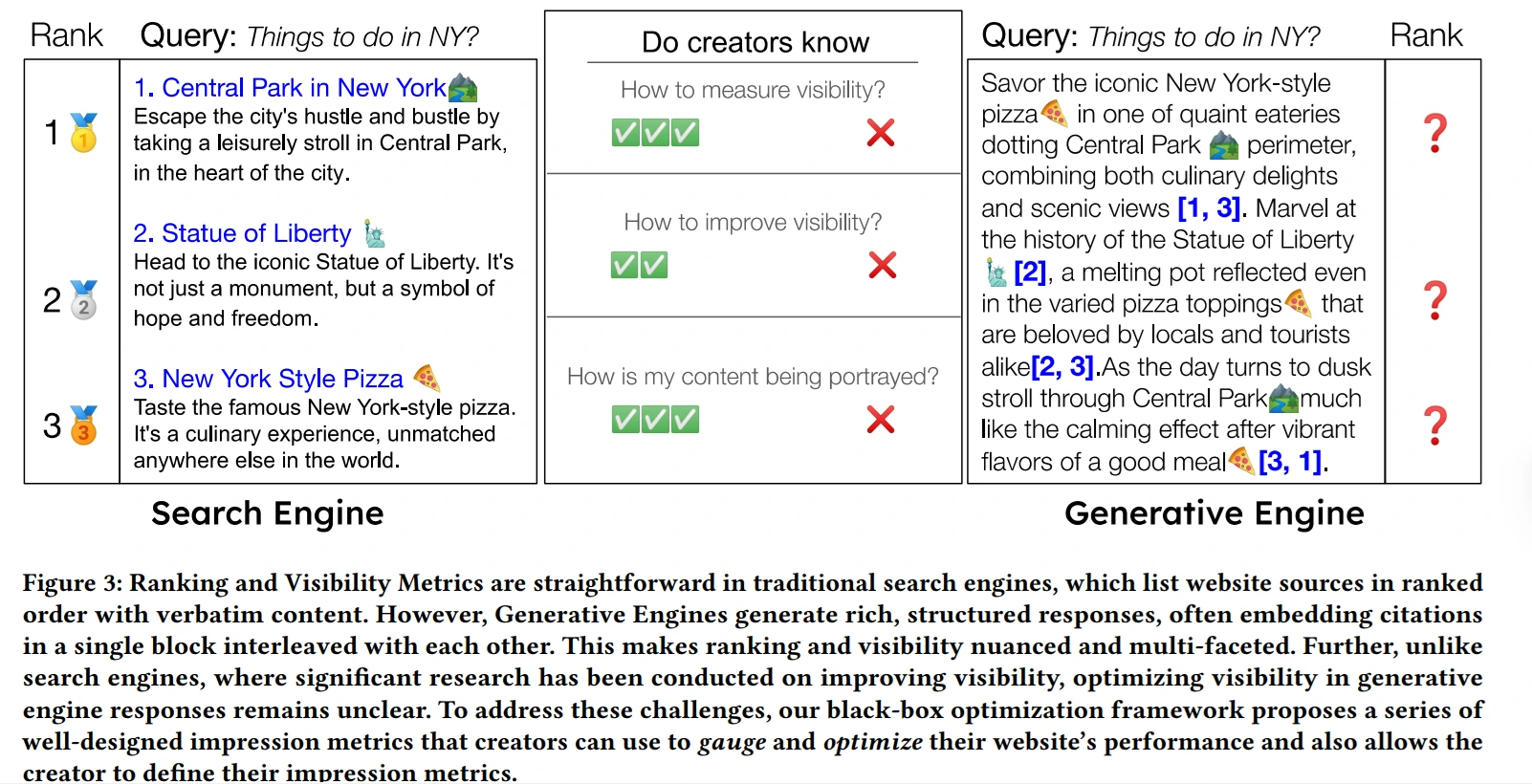
Visibility Metrics for Generative Engines
Unlike traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO), where ranking positions are the primary indicators of success, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) necessitates a more nuanced and multi-dimensional approach to measuring visibility. The way a generative engine presents information is far richer than a simple list of links, making it crucial to adopt metrics tailored to this environment.
- Word Count (and Position-Adjusted Word Count): Measuring Representation Volume and Impact: This straightforward metric counts the number of words extracted from a particular website (or source) that are included in the generative engine’s response. A higher word count generally indicates a greater level of relevance and contribution to the answer provided. It signals that the source played a prominent role in the synthesis of the information. Position-Adjusted Word Count, in contrast, recognizes that words at the beginning of the answer may have more weight to a user than those at the end. In that regard, we propose a position-adjusted count that reduces the weight by an exponentially decaying function of the citation position.
- Subjective Impression (Powered by LLM-Based Evaluation): This more holistic metric attempts to quantify the overall quality of the impression that a source leaves on the user. Rather than merely counting words or positions, it assesses the degree to which the source is perceived as valuable, relevant, and informative. The best way to measure Subjective Impression is by having an LLM model (such as GPT-4 or Google Gemini) score the quality of the impression of each website or citation with respect to the query or the whole answer. Many subjective factors may influence the value of Subjective Impression:
- Relevance to the user query: Does the cited sentence directly answer the user’s query?
- Influence of the citation: Does the generated response heavily rely on the information provided by the citation?
- Uniqueness of the cited Material: Does the citation provide novel material or repeat the same facts?
- Subjective position: How does the user perceive the position of the source in the answer? Is it prominent?
- Subjective Count: How does the user perceive the volume of content provided by the source? Is it small or high?
- Probability of Click: What are the chances that the user will click on the source? Is it a trusted source or a novel source?
- Diversity: Does the source enable more diverse answers and opinions?
- Citation Frequency and Placement: Citation frequency tracks how often a source is referenced throughout a GE’s response, indicating the source’s perceived authority or comprehensiveness. Moreover, the placement of these citations – whether near the start, within key arguments, or in the concluding remarks – plays a vital role in influencing user perception. Strategic placement underscores a source’s significance and enhances its overall impact.
- Domain Authority & User Trust Signals: While direct measurement within a black-box system can be challenging, integrating external indicators such as domain authority (measured by tools like Moz or Ahrefs) and user trust signals (e.g., ratings, reviews) can provide valuable context. A GE is more likely to elevate sources from reputable domains and those with high user satisfaction scores, as these metrics serve as proxies for content quality and trustworthiness.
- Content Engagement Signals: Tracking user engagement metrics (where possible and ethical), such as time spent reading content on the source website (if linked by the GE), social shares, and comments, offers insights into the resonance of the source material. High engagement suggests that the content is valuable and resonates with users, which may influence the GE’s future weighting of that source.
- Multimodal Elements (Image/Video Inclusion): In GEs capable of incorporating images, videos, or interactive elements, the inclusion of such multimedia from a particular source dramatically enhances its visibility and engagement. Tracking the frequency and prominence of multimedia elements extracted from a given source is, therefore, an important visibility indicator.
GEO Strategies for Content Creators
After understanding the core principles of GEO and identifying relevant visibility metrics, the next critical step is to implement effective strategies to optimize content for generative engines. These strategies can be broadly categorized as either content enhancement or stylistic alterations.
I. Content Enhancement Strategies: Adding Substance and Value
These strategies focus on improving the overall quality and depth of the information presented, making it more attractive to generative engines and more valuable to users.
- Statistics Addition: Generative engines often prioritize factual, data-driven content. Incorporating relevant statistics, charts, and graphs can significantly enhance a website’s visibility. Example: Instead of stating “Online shopping is popular,” revise to “According to a recent study by Statista, online shopping sales are projected to reach $5.5 trillion in 2024.” Link directly to that specific report on Statista from your website.
- Actionable Insight: Research credible sources for statistics relevant to your niche and embed them seamlessly within your content. Make the data visually engaging through charts or infographics.
- Example: Adding a statistic about increased crop yields from using a certain pesticide or fertilizer for an agriculture website.
- Quotation Addition: Adding compelling and insightful quotes from experts or credible sources can enhance the credibility and persuasiveness of your content.
- Actionable Insight: Identify thought leaders and authoritative figures in your field. Carefully select quotes that support your arguments and provide unique insights.
- Example: For an article discussing the future of remote work, include a quote from a leading expert in workplace trends.
- Citation Addition: Explicitly citing reliable sources for all factual claims and supporting evidence is crucial for building trust with generative engines and users.
- Actionable Insight: Meticulously document all sources used in your content. Provide direct links to the original sources whenever possible.
- Example: If describing the historical context of a specific event, cite reputable historical documents and academic publications.
- Multimodal Content Integration: GEs can often ingest and display images, videos, and other multimedia elements. Integrating these elements strategically can significantly improve engagement and visibility.
- Actionable Insight: Include relevant images, videos, and interactive elements that enhance the user experience and provide additional context. Ensure that all multimedia elements are properly optimized for search engines (e.g., using descriptive file names, alt tags, and captions).
- Example: Embed a short explanatory video within a blog post, or include relevant infographics, or perhaps podcasts.
- Structured Data Markup: Using schema markup is like adding metadata for search engines to understand the context of your website.
- Actionable Insight: Use schema markup to tell search engines what your page is about, such as a product page, a blog post, or a recipe.
- Answering Common Questions: By anticipating and directly answering common user questions related to your niche, you can position your content as a valuable resource for generative engines.
- Actionable Insight: Conduct keyword research to identify the most frequently asked questions in your field. Create dedicated FAQ sections within your content or develop entire articles dedicated to answering specific questions in a clear and comprehensive manner.
- Example: A business website creates pages addressing frequently asked questions from clients.
II. Stylistic Alteration Strategies: Enhancing Readability and Persuasiveness
These strategies focus on improving the presentation and clarity of the content, making it more appealing to both generative engines and human readers.
- Authoritative Tone: Generative engines tend to favor content that is perceived as credible and authoritative. Adopting a confident, well-informed writing style can significantly improve visibility.
- Actionable Insight: Base your arguments on solid evidence and cite reliable sources. Avoid using overly tentative language or expressing personal opinions without justification.
- Example: Use formal language, cite evidence, and mention relevant experts in your field.
- Easy-to-Understand Language: Simplifying complex concepts and using clear, concise language can make your content more accessible to a wider audience, including generative engines.
- Actionable Insight: Avoid jargon and technical terms unless absolutely necessary. When using technical terms, provide clear explanations. Use short sentences and paragraphs to improve readability.
- Example: Avoid complex vocabulary and explain technical terms using simple, easy-to-understand words.
- Fluency Optimization: Content that is well-written, grammatically correct, and flows smoothly is more likely to be favored by generative engines.
- Actionable Insight: Proofread your content carefully for errors in grammar and spelling. Read your content aloud to identify areas where the flow can be improved.
- Example: A professional writer or editor is hired to review and edit a text to optimize its quality.
- Use Technical Terms/Keywords Judiciously: SEO practices still require careful consideration when choosing and using relevant keywords, and technical terms.
- Actionable Insight: Conduct keyword research to identify the terms that users are most likely to search. Incorporate those keywords strategically throughout your content, but avoid overstuffing or using them unnaturally.
- Example: Optimize the title, meta description, headings, and first paragraph of the content to maximize its SEO.
- Create Compelling Headlines and Meta Descriptions: Well-crafted headlines and meta descriptions can significantly increase the click-through rate of your content from search engine results, signaling to generative engines that your content is valuable and relevant.
- Actionable Insight: Use strong keywords, numbers, and action verbs to create headlines and meta descriptions that capture attention and accurately reflect the content.
By implementing these expanded GEO strategies, content creators can significantly improve their visibility within generative engine responses, ensuring that their content continues to reach a wide audience in the evolving digital landscape. Remember that ongoing monitoring and adaptation are crucial for maintaining a strong online presence in this dynamic environment.
Introducing GEO-BENCH: A Comprehensive Benchmark
To facilitate systematic evaluation of GEO methods, we introduce GEO-BENCH, a large-scale benchmark consisting of diverse user queries across multiple domains. GEO-BENCH provides a standardized platform for:
- Evaluating GE Performance: Assessing the accuracy, completeness, and relevance of responses generated by GEs.
- Comparing GEO Methods: Comparing the effectiveness of different optimization strategies in improving content visibility.
- Identifying Best Practices: Uncovering optimal strategies for different content types and domains.
GEO-BENCH includes queries from a variety of sources, including MS Macro, ORCAS-1, Natural Questions, AllSouls, LIMA, Davinci-Debate, Perplexity.ai Discover, ELI-5, and GPT-4 Generated Queries. Each query is tagged with relevant categories to enable domain-specific analysis.
Experimental Results and Analysis
Experiments conducted using GEO-BENCH demonstrate the effectiveness of GEO methods in improving content visibility. Our results show that GEO can boost visibility by up to 40% on diverse queries. Notably, adding citations, quotations, and statistics to website content significantly enhances its visibility within GE responses. We also find that stylistic changes, such as improving fluency and readability, can also lead to substantial improvements.
Furthermore, our analysis reveals that the effectiveness of GEO strategies varies across domains. For example, Authoritative significantly improves performance in debate-style questions and queries related to history. Similarly, the addition of citations is particularly beneficial for factual questions.

GEO in the Wild: Experiments with Deployed Generative Engines
To validate our findings in a real-world setting, we evaluated GEO methods on Perplexity.ai, a commercially deployed GE with a large user base. Our results on Perplexity.ai mirrored those obtained using our simulated GE, further highlighting the potential impact of GEO in the real world.
The Future of GEO
As GEs continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the field of GEO will undoubtedly grow and adapt. Future research in GEO may focus on:
- Developing More Sophisticated Visibility Metrics: Capturing the full range of factors that influence content visibility in GEs.
- Automating GEO Strategies: Creating AI-powered tools that automatically analyze and optimize website content for GEs.
- Exploring New Optimization Techniques: Discovering innovative ways to enhance content visibility, such as multimodal content integration.
- Addressing Ethical Considerations: Developing guidelines and best practices for responsible GEO.
Conclusion
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents a paradigm shift in how content creators can maintain visibility and relevance in the age of generative AI. By understanding the principles of GEO, employing effective optimization strategies, and leveraging comprehensive benchmarks like GEO-BENCH, content creators can ensure that their voices are heard and their contributions are recognized in the evolving digital landscape. As generative engines continue to reshape the future of information discovery, GEO will play a critical role in fostering a healthy, equitable, and vibrant digital ecosystem.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of GEO, highlighting its key principles, framework, strategies, and potential impact. It is designed to educate content creators, researchers, and developers about this emerging field and encourage further exploration and innovation.
Source: this article is an adaptation of the scientific paper : GEO: Generative Engine Optimization



